Game Based Learning

We can define technology as the use of various tools to produce results [1]. Young learners use a computer for both entertainment, as well as a learning tool [2]. The use of technology among small groups is directly proportional to the increase in problem-solving skills and positive interactions [3]. It was also observed that they benefit both socially and emotionally, due to the shared interactions when teachers are actively involved with them during the use of these technologies [4]. Therefore, communication with supportive adults while using these platforms can have positive results [5]. The internet and technology platforms are a very good source for research, information, learning and understanding. School and university teachers who include technology in the classrooms with appropriate guidance and support, including relevant experiences with young learners, provide an enhanced and rich learning environment [6].
As there is an increase in use of technological resources in our daily lives, it has led to their implementation in our lectures [7]. It has been observed that the use of these tools improves the participation and motivation among students, thereby increasing the meaningful learning in students [8]. The desire to learn increases due to the use of technologies with which students are familiar with [9]. Online platforms like Socrative, Quizlet, Quizziz and Kahoot that apply game based learning have become more popular in the field of education, and these platforms are now widely used to promote student learning [10]. Kahoot platform is an excellent ICT (Information and communications technology) which can be used to conduct educational surveys, quizzes and discussions, generating response. Research shows that the use of web-based Kahoot tool in the classroom has the benefit of improving the students learning process and their overall participation, along with bringing about a positive relationship among class members and development of social skills [11].
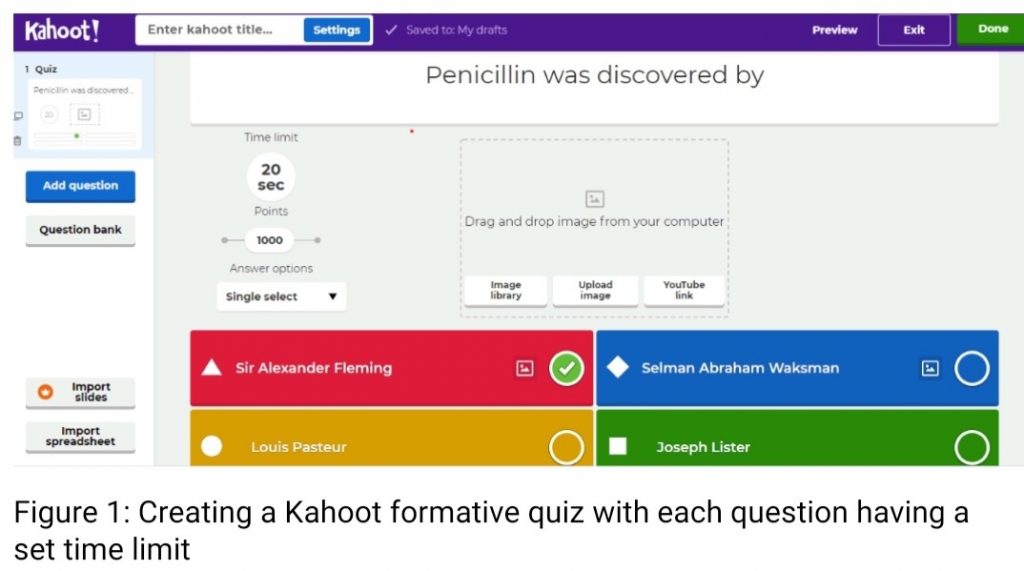
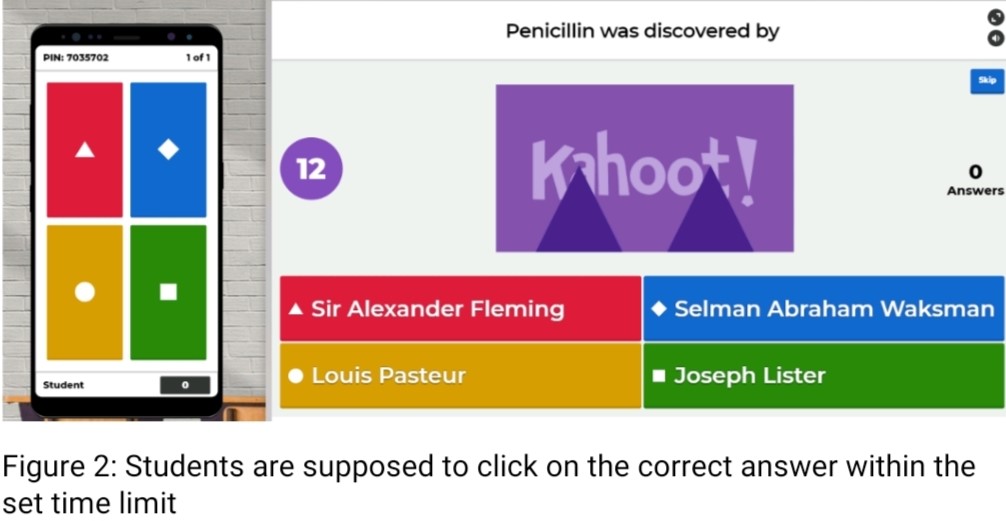
The purpose of assessment is to gather and record relevant information regarding the performance or progress of learners, which can be used as a guidance during the learning process [12]. We usually have the summative and formative types of assessment. Summative assessments are conducted after the syllabus in a particular term is completed, and it requires grading so that judgements can be made about the learning and understanding that has occurred during that semester. Whereas formative assessments are designed to improve the student’s understanding of the subject matter [13]. Thus a formative assessment is a part of learning and is prepared to provide appropriate feedback for improvement in performance, and accelerate learning [12]. The type of assessment for which the Kahoot platform can be used is the formative assessment. Kahoot is now a popular real-time platform for game based learning that is widely used in schools and universities, with reports of more than 30 million users worldwide [14].
The rationale for using this assessment method is due to the benefits of game based learning [15]. Studies have shown that game based learning results in significantly improved student performance and focus compared to traditional methods [16]. This includes better learning efficiency [17], increase in student motivation and interest [18], good engagement [19], and providing an effective feedback [20].
As most teachers have been conducting quizzes and surveys in classroom using traditional methods, it can be challenging for a few of them to design the technology enabled formative assessments, as most of these ICT tools are recently developed, and they find it laborious to use all these various technology platforms. Even though integrating these tools may be challenging in the beginning, but if used in creative ways it could support curiosity, attention and understanding in learning, among students. Regular use of these tools will benefit both, the teacher and the learner, and in the long run it is very productive, satisfying and rewarding.
This article is contributed by Dr. Sunesh K. Augustine, Senior Lecturer, MDIS School of Life Sciences.
References:
- Snider, S., Hirschy, S. A self-reflection framework for technology use by classroom teachers of young learners. He Kupu. 2009, 2, 30-44
- Yelland, N. Technology as Play. Early Childhood Education Journal. 1999,26(4), 217-220.
- Lomangino, A. G., Nicholson, J., Sulzby, E. The influence of power relations and social goals on children’s collaborative interactions while composing on computer. Early Childhood Research Quarterly, 1999, 14(2), 197-228.